Holotopia
Contents
HOLOTOPIA
An Actionable Strategy
Imagine...
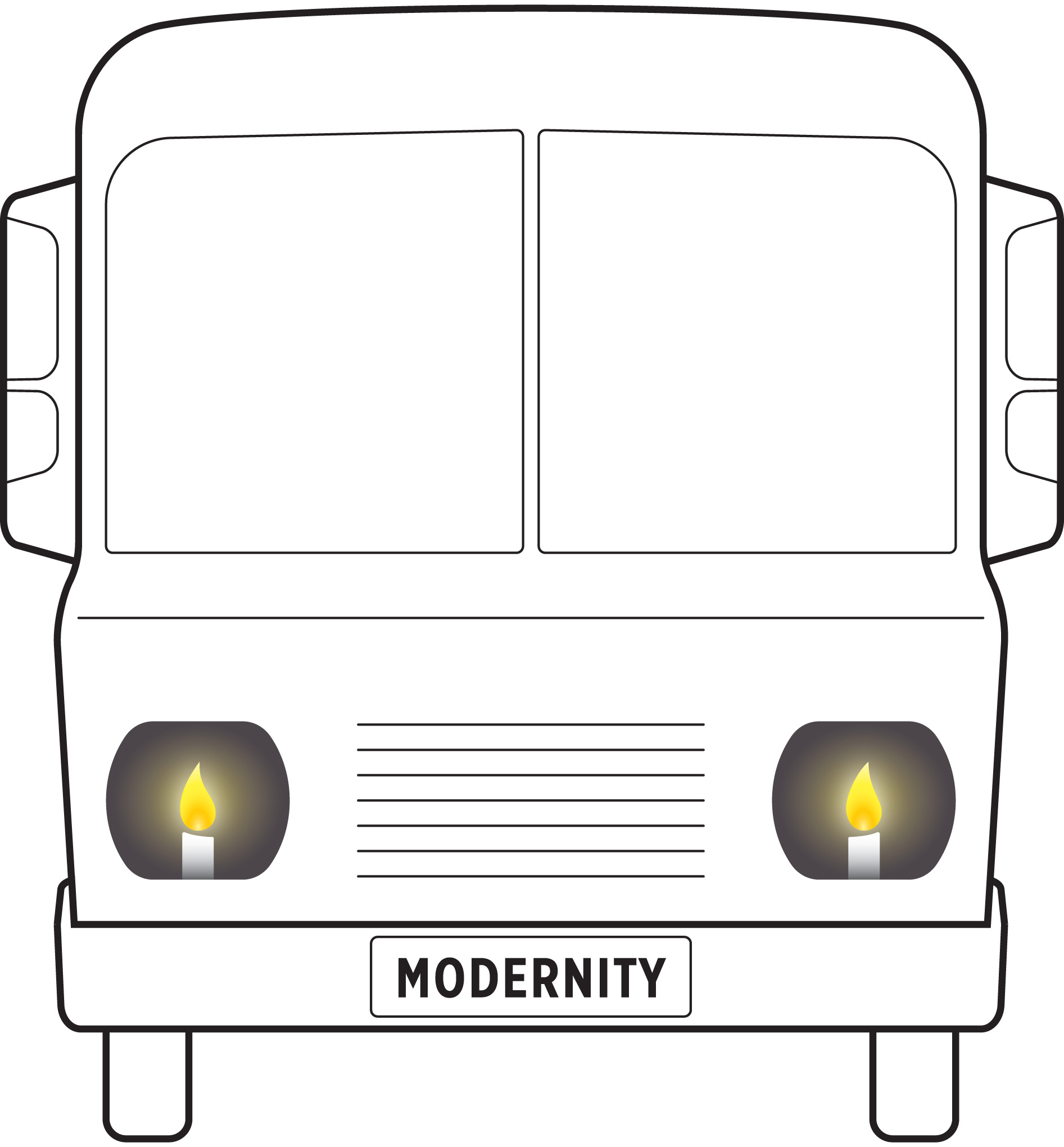
You are about to board a bus for a long night ride, when you notice the flickering streaks of light emanating from two wax candles, placed where the headlights of the bus are expected to be. Candles? As headlights?
Of course, the idea of candles as headlights is absurd. So why propose it?
Because on a much larger scale this absurdity has become reality.
The Modernity ideogram renders the essence of our contemporary situation by depicting our society as an accelerating bus without a steering wheel, and the way we look at the world, try to comprehend and handle it as guided by a pair of candle headlights.
Our proposal
The core of our knowledge federation proposal is to change the relationship we have with information.
What is our relationship with information presently like?
Here is how Neil Postman described it:
"The tie between information and action has been severed. Information is now a commodity that can be bought and sold, or used as a form of entertainment, or worn like a garment to enhance one's status. It comes indiscriminately, directed at no one in particular, disconnected from usefulness; we are glutted with information, drowning in information, have no control over it, don't know what to do with it."
What would information and our handling of information be like, if we treated them as we treat other human-made things—if we adapted them to the purposes that need to be served?
By what methods, what social processes, and by whom would information be created? What new information formats would emerge, and supplement or replace the traditional books and articles? How would information technology be adapted and applied? What would public informing be like? And academic communication, and education?
The substance of our proposal is a complete prototype of knowledge federation, where initial answers to relevant questions are presented, and in part implemented in practice.
Our call to action is to institutionalize and develop knowledge federation as an academic field, and a real-life praxis (informed practice).
Our purpose is to restore agency to information, and power to knowledge.
A proof of concept application
The Club of Rome's assessment of the situation we are in, provided us with a benchmark challenge for putting the proposed ideas to a test.
Four decades ago—based on a decade of this global think tank's research into the future prospects of mankind, in a book titled "One Hundred Pages for the Future"—Aurelio Peccei issued the following call to action:
"It is absolutely essential to find a way to change course."
Peccei also specified what needed to be done to change course:
"The future will either be an inspired product of a great cultural revival, or there will be no future."
This conclusion, that we are in a state of crisis that has cultural roots and must be handled accordingly, Peccei shared with a number of twentieth century's thinkers. Arne Næss, Norway's esteemed philosopher, reached it on different grounds, and called it "deep ecology".
In "Human Quality", Peccei explained his call to action:
"Let me recapitulate what seems to me the crucial question at this point of the human venture. Man has acquired such decisive power that his future depends essentially on how he will use it. However, the business of human life has become so complicated that he is culturally unprepared even to understand his new position clearly. As a consequence, his current predicament is not only worsening but, with the accelerated tempo of events, may become decidedly catastrophic in a not too distant future. The downward trend of human fortunes can be countered and reversed only by the advent of a new humanism essentially based on and aiming at man’s cultural development, that is, a substantial improvement in human quality throughout the world."
The Club of Rome insisted that lasting solutions would not be found by focusing on specific problems, but by transforming the condition from which they all stem, which they called "problematique".
Could the change of 'headlights' we are proposing be "a way to change course"?
A vision
Holotopia is a vision of a possible future that emerges when proper light has been turned on.
Since Thomas More coined this term and described the first utopia, a number of visions of an ideal but non-existing social and cultural order of things have been proposed. But in view of adverse and contrasting realities, the word "utopia" acquired the negative meaning of an unrealizable fancy.
As the optimism regarding our future waned, apocalyptic or "dystopian" visions became common. The "protopias" emerged as a compromise, where the focus is on smaller but practically realizable improvements.
The holotopia is different in spirit from them all. It is a more attractive vision of the future than what the common utopias offered—whose authors either lacked the information to see what was possible, or lived in the times when the resources we have did not yet exist. And yet the holotopia is readily realizable—because we already have the information and other resources that are needed for its fulfillment.
The holotopia vision is made concrete in terms of five insights, as explained below.
A principle
What do we need to do to change course toward the holotopia?
The five insights point to a simple principle or rule of thumb—making things whole.
This principle is suggested by the holotopia's very name. And also by the Modernity ideogram. Instead of reifying our institutions and professions, and merely acting in them competitively to improve "our own" situation or condition, we consider ourselves and what we do as functional elements in a larger system of systems; and we self-organize, and act, as it may best suit the wholeness of it all.
Imagine if academic and other knowledge-workers collaborated to serve and develop planetary wholeness – what magnitude of benefits would result!
A method
"The arguments posed in the preceding pages", Peccei summarized in One Hundred Pages for the Future, "point out several things, of which one of the most important is that our generations seem to have lost the sense of the whole."
To make things whole—we must be able to see them whole!
To highlight that the knowledge federation methodology described and implemented in the proposed prototype affords that very capability, to see things whole, in the context of the holotopia we refer to it by the pseudonym holoscope.
While the characteristics of the holoscope—the design choices or design patterns, how they follow from published insights and why they are necessary for 'illuminating the way'—will become obvious in the course of this presentation, one of them must be made clear from the start.
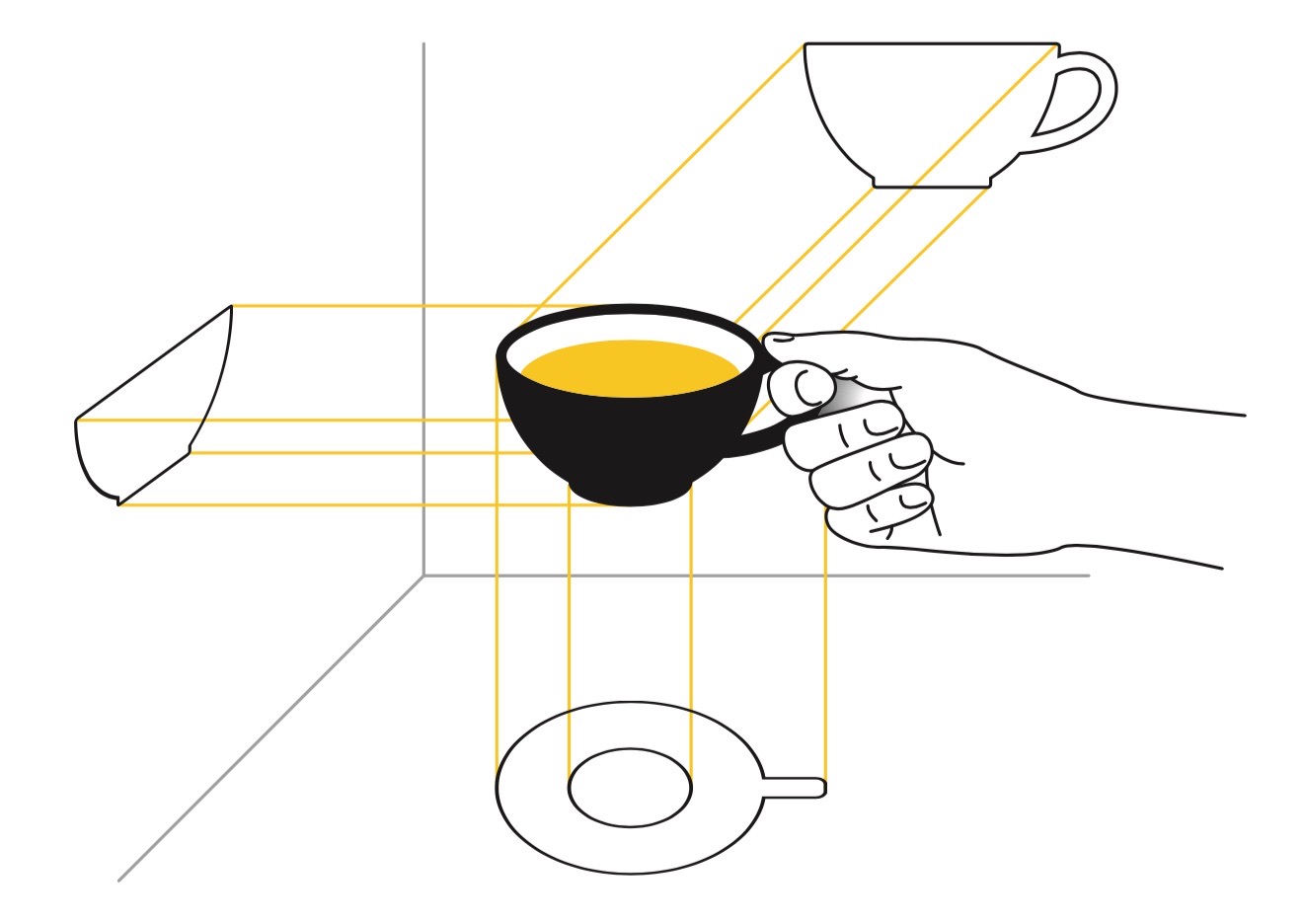
To see things whole, we must look at all sides.
The holoscope distinguishes itself by allowing for multiple ways of looking at a theme or issue, which are called scopes. The scopes and the resulting views have similar meaning and role as projections do in technical drawing.
This modernization of our handling of information—distinguished by purposeful, free and informed creation of the ways in which we look at the world—has become necessary in our situation, suggests the bus with candle headlights metaphor. But it also presents a challenge to the reader—to bear in mind that the resulting views are not offered as "reality pictures", contending for that status with one another.
In the holoscope, the legitimacy and peaceful coexistence of multiple ways to look at a theme is axiomatic.
We shall continue to use the conventional language and say that X is Y—although it would be more correct to say that X can or must (also) be seen as Y. The views we offer are accompanied by an invitation to genuinely try to look at the theme at hand in a certain specific way; and to do that collaboratively, in a dialog.
To liberate our worldview from the inherited concepts and methods and allow for deliberate choice of scopes, we used the scientific method as venture point—and modified it by taking recourse to insights reached in 20th century science and philosophy.
Science gave us new ways to look at the world: The telescope and the microscope enabled us to see the things that are too distant or too small to be seen by the naked eye, and our vision expanded beyond bounds. But science had the tendency to keep us focused on things that were either too distant or too small to be relevant—compared to all those large things or issues nearby, which now demand our attention. The holoscope is conceived as a way to look at the world that helps us see any chosen thing or theme as a whole—from all sides; and in proportion.
A discovery of a new way of looking—which reveals a structural problem, and helps us reach a correct general assessment of an object of study or a situation (whether the 'cup' is 'whole' or 'broken') is a new kind of result that is made possible by the general-purpose science, modeled by the holoscope
To see more, we take recourse to the vision of others. The holoscope combines scientific and other insights to enable us to see what we ignored, to 'see the other side'. This allows us to detect structural defects ('cracks') in core elements of everyday reality—which when we see them in our habitual way ('in the light of a candle'), appear to us as just normal.
All elements in our proposal are deliberately left unfinished, rendered as a collection of prototypes. Think of them as composing a cardboard map of a city, and a construction site. By sharing them, we are not making a case for building a specific 'city'—but for 'architecture' as an academic field, and a real-life praxis.
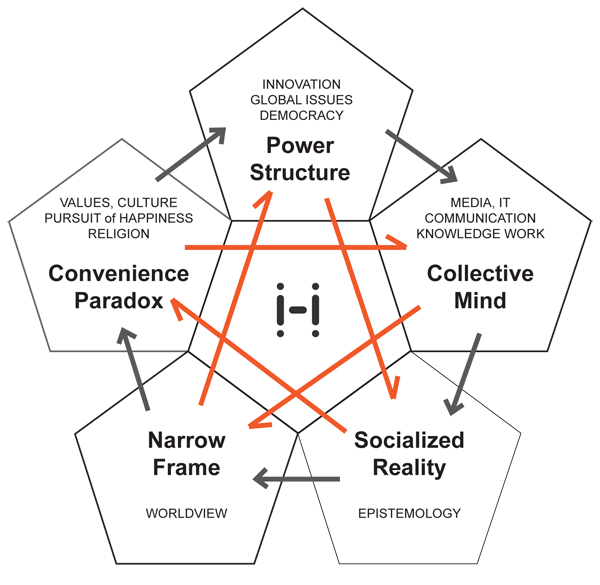
Five insights
Scope
What is wrong with our present "course"? In what ways does it need to be changed? What benefits will result?
We use the holoscope to illuminate five pivotal themes, which determine the "course":
- Innovation—the way we use our ability to create, and induce change
- Communication—the social process, enabled by technology, by which information is handled
- Epistemology—the fundamental assumptions we use to create truth and meaning, or "the relationship we have with information"
- Method—the way in which truth and meaning are constructed in everyday life, or "the way we look at the world, try to comprehend and handle it"
- Values—the way we "pursue happiness", which in the modern society directly determines the course
In each case, we see a structural defect, which led to perceived problems.
Those structural defects can and must be remedied.
Their removal naturally leads to improvements that are well beyond the removal of symptoms.
The holotopia vision results.
From the five insights a sixth insight follows—that the more basic problem that underlies our problems is that "the tie between information and action has been severed". And that the key to solution, the "systemic leverage point" for "changing course" and continuing to evolve culturally and socially, in a new way, is the same as it was in Galilei's time: We must once again "change the relationship we have with information".
A case for our proposal is thereby also made.
In the spirit of the holoscope, we here only summarize each of the five insights—and provide evidence and details separately.
Scope
What do we need to do, to become capable of "changing course"?
"Man has acquired such decisive power that his future depends essentially on how he will use it", observed Peccei. Imagine if some malevolent entity, perhaps an insane dictator, took control over that power.
The power structure insight shows that no dictator is needed.
Albeit in democracy, we are in that situation already.
While the nature of the power structure will become clear as we go along, imagine it, to begin with, as our institutions; or more accurately, as the systems in which we live and work (which we simply call systems).
Notice that systems have an immense power—over us, because we have to adapt to them to be able to live and work; and over our environment, because by organizing us and using us in a certain specific way, they decide what the effects of our work will be.
The power structure determines whether the effects of our efforts will be problems, or solutions.
Diagnosis
How suitable are the systems in which we live and work for their all-important role?
Evidence shows that they waste a lion's share of our resources. And that they either cause problems, or make us incapable of solving them.
The root cause of this malady is readily found in the way in which systems evolve.
Survival of the fittest favors the systems that are predatory, not the ones that are useful.
This excerpt from Joel Bakan's documentary "The Corporation" (which Bakan as a law professor created to federate an insight he considered essential) explains how the most powerful institution on our planet evolved to be a perfect "externalizing machine" ("Externalizing" means maximizing profits by letting someone else bear the costs, notably the people and the environment), just as the shark evolved to be a perfect "killing machine". This scene from Sidney Pollack's 1969 film "They Shoot Horses, Don't They?" will illustrate how the power structure affects our own condition.
The systems provide an ecology, which in the long run shapes our values, and our "human quality". They have the power to socialize us in way that suit their needs. "The business of business is business"—and if our business will succeed in competition, we must act in a certain way. We either bend and comply—or get replaced. The effect on the system is the same.
A consequence, Zygmunt Bauman diagnosed, is that bad intentions are no longer needed for bad things to happen. Through socialization, the power structure can co-opt our duty and commitment; and even our heroism and honor.
Bauman's insight that even the holocaust was only a consequence and a special case, however extreme, of (what we are calling) the power structure, calls for careful contemplation: Even the concentration camp employees, Bauman argued, were only "doing their job"—in a system whose nature and purpose was beyond their ethical sense, and power to change.
While our ethical sensitivity is tuned to the power structures of the past, we are committing, in all innocence, the greatest massive crime in human history.
Our children may not have a livable planet to live in.
Not because someone broke the rules—but because we follow them.
Remedy
The fact that we will not "solve our problems" unless we develop the capability to update our systems has not remained unnoticed.
The very first step that the The Club of Rome's founders did after its inception, in 1968, was to convene a team of experts, in Bellagio, Italy, to develop a suitable methodology. They gave "making things whole" on the scale of socio-technical systems the name "systemic innovation"—and we adapted that as one of our keywords.
The work and the conclusions of this team were based on results in the systems sciences. More recently, in "Guided Evolution of society", systems scientist Béla H. Bánáthy did a thorough job federating the relevant research, and reached this truly holotopian conclusion::
We are the first generation of our species that has the privilege, the opportunity and the burden of responsibility to engage in the process of our own evolution. We are indeed chosen people. We now have the knowledge available to us and we have the power of human and social potential that is required to initiate a new and historical social function: conscious evolution. But we can fulfill this function only if we develop evolutionary competence by evolutionary learning and acquire the will and determination to engage in conscious evolution. These two are core requirements, because what evolution did for us up to now we have to learn to do for ourselves by guiding our own evolution.
In 2010, Knowledge Federation began to self-organize to become able to make make further progress on this creative frontier. The procedure we developed is simple: We create a prototype of a system, and organize a transdisciplinary community and project around it, to update it continuously. This enables the insights reached in the participating disciplines to have real or systemic impact directly.
Our very first project of this kind, the Barcelona Innovation Ecosystem for Good Journalism in 2011, developed a prototype of a public informing that turns perceived problems (that people report directly, through citizen journalism) into systemic understanding of causes and recommendations for action (developed by involving academic and other domain experts, and having their insights made accessible by a communication design team).
The experience with this prototype revealed a general paradox we were not aware of: The senior domain experts we brought together to represent (in this case) journalism cannot change their own system (their full capacity is engaged in performing their role within the system). What they, however, can and need to do is empower their next-generation (students, junior colleagues, entrepreneurs...) to do that. A year later we created The Game-Changing Game as a generic way to do that—and hence as a "practical way to craft the future". We subsequently created The Club of Zagreb, as an update (necessary, according to this insight) of The Club of Rome. The Holotopia project builds further on the results of this work.
Our portfolio contains about forty prototypes, each of which illustrates systemic innovation in a specific domain. Each prototype is composed by weaving together design patterns—problem-solution pairs, which are ready to be adapted to other design challenges and domains.
The Collaborology prototype, in education, will highlight some of the advantages of this approach.
An education that prepares people for yesterday's professions, and only in a certain stage of life, is obviously an obstacle to systemic change. Collaborology implements an education that is in every sense flexible (self-guided, life-long...), and in an emerging area of interest (collaborative knowledge work, as enabled by new technology). By being collaboratively created itself (Collaborology is created and taught by a network of international experts, and offered to learners world-wide), the economies of scale result that dramatically reduce effort. This in addition provides a sustainable business model for developing and disseminating up-to-date knowledge in any domain of interest. By conceiving the course as a design project, where everyone collaborates on co-creating the learning resources, the students get a chance to exercise their "human quality". This in addition gives the students an essential role in the resulting 'knowledge-work ecosystem' (as 'bacteria', extracting 'nutrients') .